Chapter Overview: The World Population
This page serves as a comprehensive guide to Chapter 2 of the Class 12 Geography NCERT textbook, titled ‘The World Population (Distribution, Density and Growth)’. In this chapter, students explore the various aspects of population geography, including distribution patterns, density, and growth dynamics. The information presented is pivotal for a deeper understanding of human geography as outlined in Fundamentals of Human Geography.
Watch the NCERT Solution Video
To reinforce your understanding of the concepts discussed, we have included a detailed YouTube video covering the NCERT solution for this chapter. This video will provide explanations, examples, and clarification of key topics, ensuring that you grasp the essential points effectively. You can watch the video below:
Download the Free PDF and Access Other NCERT Solutions
For further study, we offer a free downloadable PDF of Chapter 2. This resource is designed to facilitate your revision and enhance your understanding through structured notes. Additionally, you can find solutions for other chapters within the NCERT syllabus to aid your preparation.
Explore more NCERT solutions and equip yourself with the knowledge needed to excel in your examinations. Together with our resources, you will be well-prepared to tackle questions on population distribution, density, and growth.
NCERT Solutions
1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
(i) Which one of the following continents has the highest growth of population?
(a) Africa
(b) South America
(c) Asia
(d) North America
Answer: (a) Africa
(ii) Which one of the following is not an area of sparse population?
(a) The Atacama
(b) South-east Asia
(c) Equatorial region
(d) Polar regions
Answer: (b) South-east Asia
(iii) Which one of the following is not a push factor ?
(a) Water shortage
(b) Medical/educational facilities
(c) Unemployment
(d) Epidemics
Answer: (d) Epidemics
(iv) Which one of the following is not a fact ?
(a) Human population increased more than ten times during the past 500 years.
(b) Population growth is high in the first stage of demographic transition
Answer: (b) Population growth is high in the first stage of demographic transition
2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) Name three geographical factors that influence the distribution of population.
Answer: Factors influencing the distribution of population are:
Geographical factors: Availability of water for various purposes from drinking to agricultural use to navigation is of utmost importance for human survival. This is the reason that all the civilizations of the world have flourished nearby rivers. Climate also plays an important role with respect to distribution of population. Areas with a comfortable climate, where there is not much seasonal variation attract more people. Areas with very heavy rainfall or extreme and harsh climates have low population. Another important factor is flat and fertile plains attract more people as such areas are favorable for agricultural production.
Social /Cultural factors: Places with religious or cultural significance attract more number of people. It may also be because of their staunch faith. In the same way – people tend to move away from places where there is social and political unrest.
Economic factors: Areas with mineral deposits attract industries and so the employment. Cities that have rapid industrialization and economic activities tend to migrate populations faster.
(ii) There are a number of areas of high population density in the world. Why does this happen?
Answer: Population density depends on several factors such as land fertility (agri-suitabilty), urbanisation, average annual rainfall, weather pattern, freshwater reserves, development of the area, sociological indicators, economic indicators etc. Throughout history some parts of the world have been found to be more densely populated than others, for the reasons discussed above, most of which revolve around the availability of food and water.
Since pre-historic times it has been found that human beings congregated and settled around places where they had relatively easy access to water and food (plants and animals). For a civilisation to flourish access to water, suitable weather and relatively plain ground that allows for agriculture are almost always essential characteristics.
(iii) What are the three components of population change?
Answer: ‘Three components of population change are:
Birth rate: The birth rate is the ratio between the number of live-born births in the year and the average total population of that year.
Death rate: The death rate is the number of people per thousand who die in a particular area during a particular period of time. Hence it is the ratio of total deaths to total population in a specified community or area over a specified period of time.
Migration: The net migration rate is the difference between the number of immigrants (people coming into an area) and the number of emigrants (people leaving an area) throughout the year. When the number of immigrants is larger than the number of emigrants, a positive net migration rate occurs. When more emigrate from a country, the result is a negative net migration rate, meaning that more people are leaving than entering the area. When there is an equal number of immigrants and emigrants, the net migration rate is balanced.
3. Distinguish between:
(i) Birth rate and death rate.
Answer:
| Birth Rate | Death Rate |
| It is the number of live births per thousand of population during a year for a particular region | It is the number of deaths per thousand of population during a year for a particular region |
| It is calculated using the following formula: CBR = Bi/P xlOOO Here, CBR = crude birth rate, Bi = Number of live births in a year, P = the estimated midyear population of that year. | It is calculated using the following formula: CDR= D/P xlOOO Here, CDR = crude death rate, D = Number of deaths in a year, P = the estimated midyear population of that year |
| If birth rate is more than death rate, it results in positive growth of population. | If death rate is more than birth rate it results in negative growth of population. |
(ii) Push factors and pull factors of migration.
Answer:
| Push factors | Pull factors |
| These factors are the ones which makes a place less attractive for human settlement. | These factors are the ones which makes a place an attractive destination for settlement. |
| These factors forces people to move out- hence face emigration. | These factors force inflow of people – hence face immigration. |
| Examples: Unemployment, poor living conditions, political turmoil, unpleasant climate, natural disasters, epidemics and socio-economic backwardness. | Examples: Better job opportunities, better living conditions, peace and stability, security of life and property and pleasant climate. |
Answer the following questions in about 150 words.
(i) Discuss the factors influencing the distribution and density of population in the world.
Answer: In most countries, there are wide regional variations in the geographic distribution of the ‘population. Population densities are different in various parts of the world. The world’s population reached 7.3 billion in mid-2015, which means that the world has added approximately one billion people in the span of the twelve years. The global population is highly dispersed over the seven continents. Most of the world’s population (about 60 per cent) lives in Asia. India’s population is ‘expected to continue growing for several decades. It is projected to reach 1.5 billion in 2030 and 1.7 billion in 2050, while that of China is likely to remain constant and then decrease slightly. Therefore, itis projected that India’s population will surpass China in the future.
The factors affecting distribution of population may broadly be grouped into the following major categories:
• Physical factors
• Demographic factors
• Socio-economic factors
• Political factors
The physical factors include, chiefly, climate, landforms, topography, soil, energy and mineral resources, accessibility in terms of distance from the coast, natural harbors, navigable rivers or canals etc. Socioeconomic factors include cultural characteristics, types of economic activities, technology used (including the type of farming), and social organization. Demographic factors include changes resulting from natural increase and migration. Factors such as political boundaries, political stability (or unrest), disturbances, controls on migration and trade, government policies and transportation facilities are considered as political factors.
(ii) Discuss the three stages of demographic transition.
Answer: Demographic transition theory can be used to describe and predict the future population of any area. The theory tells us that the population of any region changes from high births and high deaths to low births and low deaths as a society progresses from rural, agrarian and illiterate to urban, industrial and literate society. These changes occur in stages, which are collectively known as the demographic cycle.
The first stage has high fertility and high mortality rates because people reproduce more to compensate for the deaths due to epidemics and variable food supply. Population growth is slow and most people are engaged in agriculture where large families are an asset. Life expectancy is low; people are mostly illiterate and have low levels of technology. Two hundred years ago all the countries were in this stage.
In the second stage, fertility remains high in the beginning, but it declines with time. This is accompanied by reduced mortality rate. Improvements in sanitation and health conditions lead to decline in mortality. Because of this gap the net addition to population is high. This results in population explosion. Eg. Countries like India.
In the last stage, both fertility and mortality decline considerably. The population is either stable or grows slowly. The population becomes urbanized, literate and has high technical know how and deliberately controls the family size. Some countries even face negative growth of population, E.g., many Western European countries.
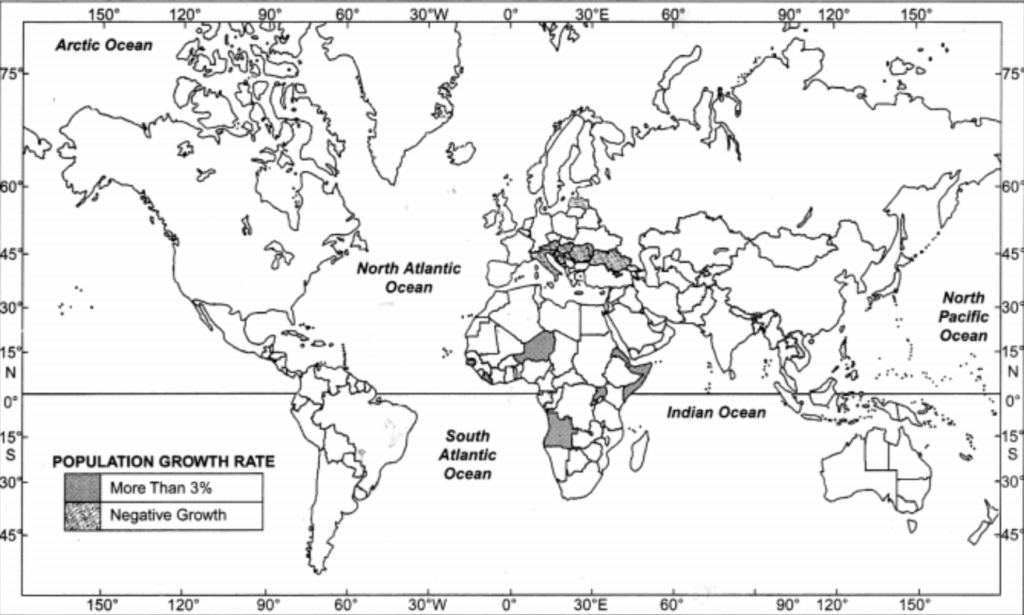
Map Skill
On an outline map of the world name the following:
(a) Countries of Europe and Asia with negative growth rate of population.
(b) African countries with growth rate of population more than three per cent.
Answer:
a. Europe: Estonia, Croatia, Romania, Bulgaria etc.
Asia : Japan, Armenia, etc.
b. Angola, Niger, Guinea, etc.