Overview of Project 2 Biodiversity Register
The Project 2 Biodiversity Register focuses on the vital aspects of biodiversity as presented in the Class 6 NCERT module on vocational education: Kaushal Bodh. This initiative aims to educate students about the importance of different biological species and their interdependence within ecosystems. Understanding these concepts can help foster a sense of responsibility towards biodiversity conservation.
Key Video Sections for Project 2
The accompanying YouTube video for the Project 2 Biodiversity Register is segmented into several informative sections. Each section comprehensively covers various themes, from the definition of biodiversity to the practical steps one can take to help preserve it. Key topics include:
- Introduction to Biodiversity
- Importance of Biodiversity
- Examples of Local Biodiversity
- Conservation Strategies
These segments provide engaging content intended to enhance student comprehension and interaction with biodiversity topics.
Question and Answer Section
To further enrich the learning experience, a structured question and answer section follows the video content. This section seeks to reinforce understanding and allow students to reflect on the information presented. Sample questions include:
- What is biodiversity and why is it important?
- Can you name three local species and their role in the ecosystem?
- What actions can individuals take to contribute to biodiversity conservation?
These questions encourage critical thinking and help students grasp the concepts learned in a practical context, solidifying their understanding of the Project 2 Biodiversity Register.
Project 2 Biodiversity Register NCERT Solutions
Table 2.1: Identifying locations where you can observe a variety of living things (Page 38)
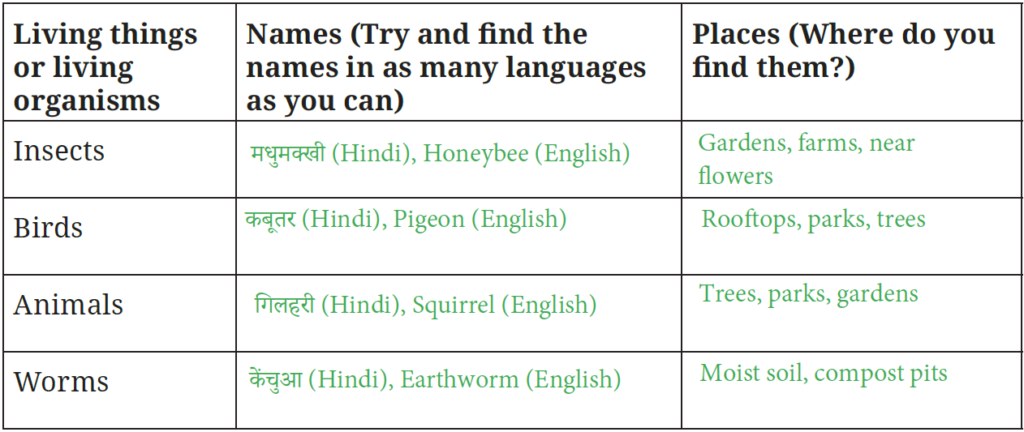
Page 39
1. Where can we find different kinds of plants in our locality?
Answer: We can find plants in gardens, farms, forests, parks, and near water bodies.
2. How do we know whether the plants growing in the locality have been there for a long time or were brought from other places?
Answer: Local people, farmers, and experts can tell if a plant is native or brought from outside.
3. Are there any plants that are no longer found in the locality?
Answer: Yes, some plants have disappeared due to urbanization, pollution, or deforestation.
4. Which kind of plants should we be growing more to support biodiversity?
Answer: We should grow native plants, medicinal herbs, and fruit trees that support birds and animals.
5. Is there any plant that we should not grow, as it harms biodiversity?
Answer: es, some invasive plants spread too fast and harm other plants, like Parthenium (Congress grass).
6. Do you have any tips for us as we start documenting our biodiversity register?
Answer: Observe carefully, ask experts for help, and record data in an organized way.
Page 40
1. What types of habitats exist in your surroundings?
Answer: Urban Parks.
2. Have you noticed any area(s) where more plants grow, compared to other areas? (Yes/No)?
Answer: Yes, places near water bodies and gardens have more plants.
3. What type of birds, mammals, insects, etc., have you observed in your surroundings?
Answer: Pigeons, sparrows, squirrels, butterflies, ants, and cows are commonly seen.
4. Are there any specific efforts being made to protect plants and animals in certain areas?
Answer: Yes, some areas have protected parks, fences, and awareness programs.
5. Now, which places do you plan to visit?
Answer: School garden, nearby park, pond, farm, and local nursery.
Table 2.2: Schedule for visits to fill biodiversity register (Page 41)

Table 2.3: Description of Crops (Page 43)
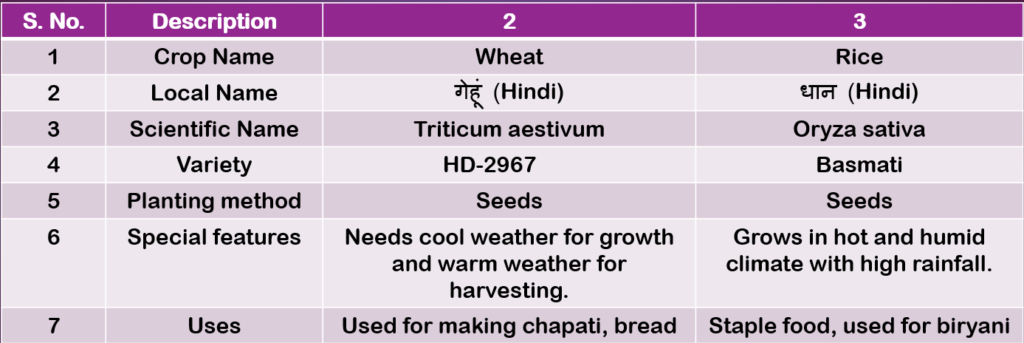
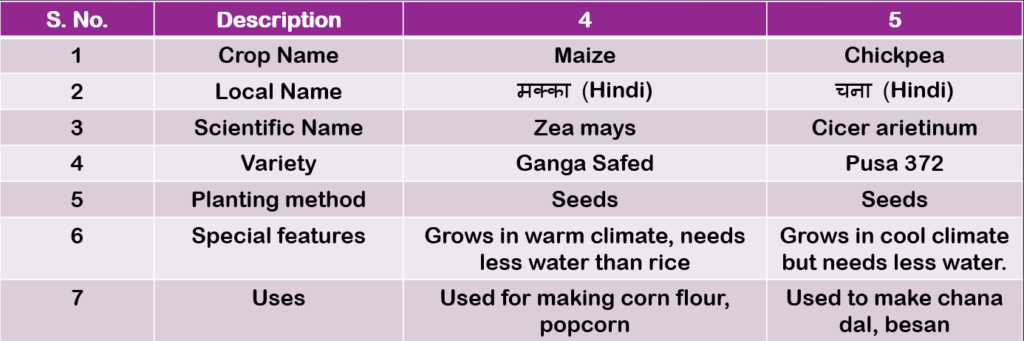
Table 2.4: Description of fruit plants (Page 44)
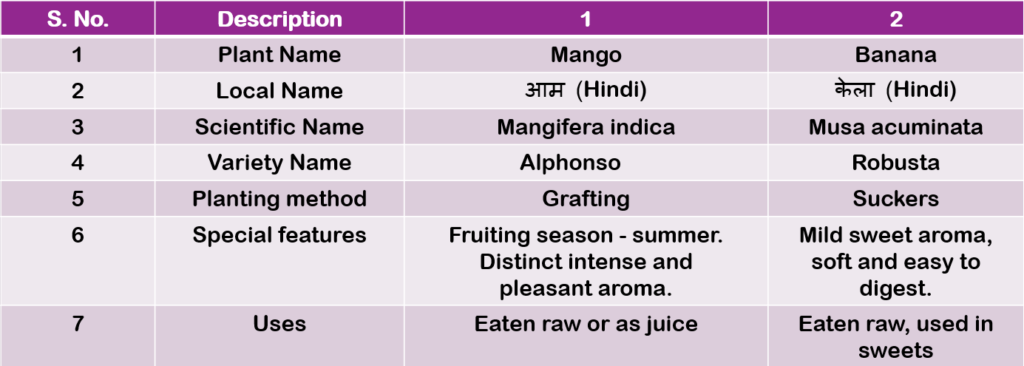

Table 2.5: Description of fodder plants (Page 44 & 45)
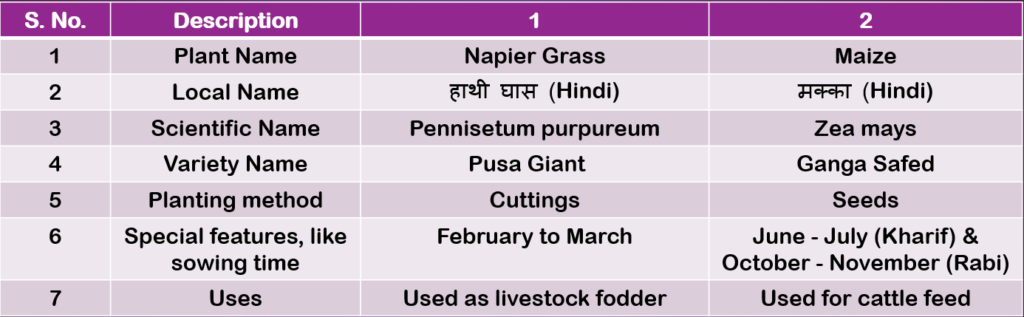
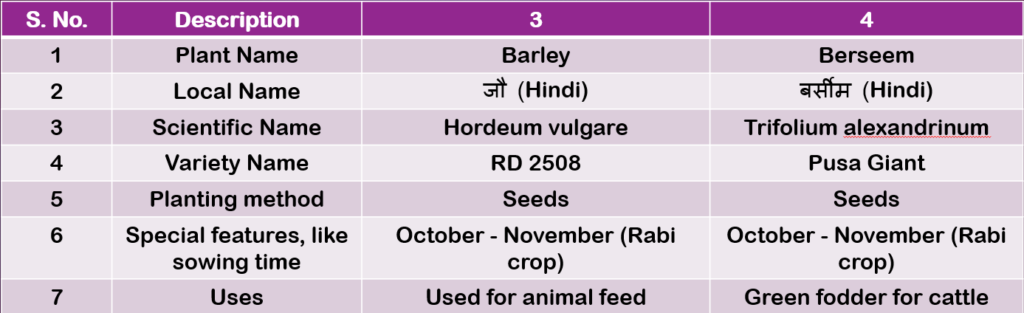
Table 2.6: Description of weed plants (Page 45)
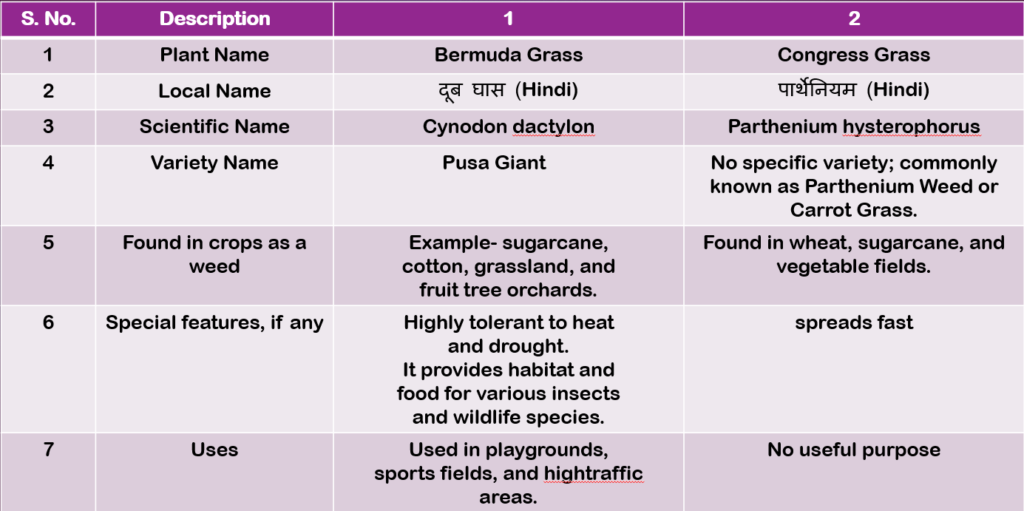
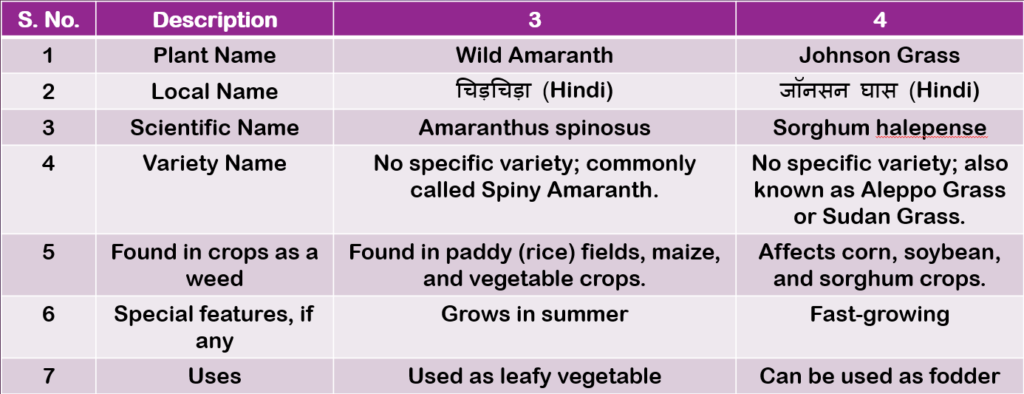
Table 2.7: Description of pests (Page 46)
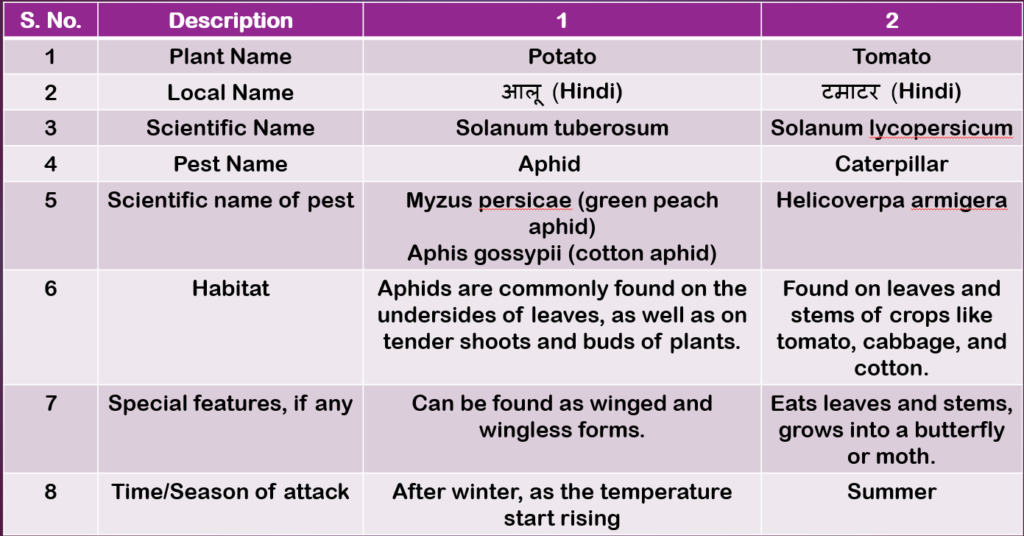
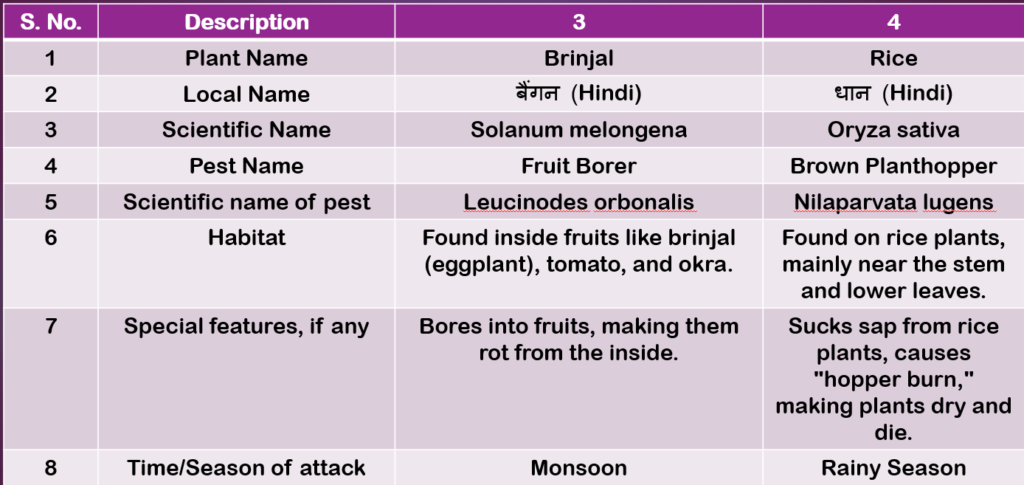
Page 48
1. What are the different plants that grow in the areas around you?
Answer: Trees (Neem, Peepal), flowering plants (Rose, Marigold), vegetables (Tomato, Spinach).
Page 49
2. Which plants grow in all seasons and which are seasonal?
Answer: Neem and Peepal trees grow in all seasons, while Mango and Mustard are seasonal.
3. Can all crops and fruits be harvested in the same season?
Answer: No, some crops grow in winter (Wheat), and some in summer (Rice, Mangoes).
4. Do all plants flower in the same season?
Answer: No, some plants flower in spring, others in winter or summer.
5. Are the plants useful for us? If yes, how?
Answer: Yes, they provide food, medicine, shelter, and fresh air.
6. Is the same fodder available throughout the year or only during some seasons?
Answer: Some fodder is available only in specific seasons, like green grass in monsoon.
7. Are all plants affected by weeds?
Answer: No, but some crops get affected by weeds like Parthenium.
8. Are some weeds useful? Name some and describe their use.
Answer: Yes, Dandelion and Fenugreek are weeds but used for food and medicine.
9. Are all plants affected by pests?
Answer: Not all, but some plants get affected by aphids, caterpillars, and insects.
10. Are plants affected by some pests more in certain seasons?
Answer: Yes, more pests attack in summer and rainy seasons.
11. What information did you gather from people in the community?
Answer: Some plants are used as medicines, like Neem for skin problems and Tulsi for cough.
Page 50
1. Did you observe more living things in one place compared to others?
Answer: Yes, parks and ponds had more birds and insects than cities.
2. How many varieties of plants and pests did you see in the places you visited?
Answer: Many types of trees, flowers, vegetables, and insects were observed.
3. Did you see the same kind of insects, pests, or worms in more than one place?
Answer: Yes, ants, butterflies, and caterpillars were found in multiple places.
4. Did you use any AI tool for this activity? If yes, which ones and how?
Answer: Google Lens was used to identify unknown plants and insects.
5. Did you use any other sources to gather information?
Answer: Yes, we used books, the internet, and asked farmers and teachers.
Page 53 (Think and Answer)
1. What did you enjoy doing?
Answer: Observing plants, recording data, and visiting different places.
2. What were the challenges you faced?
Answer: Identifying rare plants, finding scientific names, and noting seasonal changes.
3. What will you do differently next time?
Answer: Take better photos, ask more questions, and visit places in different seasons.
4. What is the importance of the biodiversity register?
Answer: It helps record plant and animal species, and understand environmental changes.
5. What jobs are related to the project?
Answer: Forest officer, scientist, conservationist, gardener, and farmer.
