Q1. If in an economy the value of Net Factor Income from Abroad is ₹200 crores and the value of Factor Income to Abroad is ₹ 40 crores. Identify the value of Factor Income from Abroad.
(a) ₹200 crore (b) ₹160 crore (c) ₹240 crore (d) ₹180 crore
Ans: (c) ₹240 crore
Q2. During COVID-19 the present government provided monetary relief to daily wage workers to meet their basic needs. While estimating National Income, how shall you treat this payment? It will be ………….. in the National income.
(a) Included (b) Not included (c) have no effect (d) None of the above
Answer – b) Not included
Q3. When Nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is ₹840 crores and price Index is 120, then the Real Gross Domestic product (GDP) will be .
(a) ₹700 crores (b) ₹900 crores (c) ₹800 crores (d) ₹500 crores
Ans (a) ₹700 crores
Q4. If the GDP deflator is 150% and real GDP is ₹ 1,100 the nominal GDP will be:
(a) ₹733 (b) ₹1,650 (c) ₹1,100 (d) ₹2,750
Ans (b) ₹1,650
Q5. A representative consumer had to spend ₹1,400 on purchase of a given basket of commodities in the year 2015-16. Due to inflation, CPI of the year 2019-20 (taking 2015-16 as base year) was 120. How much amount the consumer had to spend on purchase of the same basket of commodities in the year
2019-20?
(a) ₹1,167 (b) ₹1,680 (c) ₹1,520 (d) ₹1,280
Ans (b) ₹1,680
Q6. Which one of the following is an intermediate expenditure?
(a) Expenditure on purchase of furniture by a firm for its own use.
(b) Expenditure on maintenance by a firm.
(c) Expenditure on purchase of a tractor by a firm for its own use.
(d) Machine bought by a household.
Ans : (b) Expenditure on maintenance by a firm.
Q7. _ can be defined as the geographical territory administered by a government within which persons, goods and capital circulate freely.
(a) Political frontier (b) Economic territory
(c) National boundary (d) International frontier
Ans (b) Economic territory
Q8. “In a simplified economy, circular flow of income is based on various assumptions”. Identify, which of the following is not an assumption of circular flow of income?
(a) There are two sectors in an economy, namely- households and firms.
(b) Households are the suppliers of factor services.
(c) Firms produce goods and services.
(d) Factor income earned by households is entirely saved.
Answer: (d) Factor income earned by households is entirely saved.
Q9 Read the following statements carefully:
Statement I : Final goods include only those goods which are consumed by the households.
Statement II : Tractor purchased by a farmer can be categorized as a final good.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following:
(a) Statement I is true and statement II is false.
(b) Statement I is false and statement II is true.
(c) Both statements I and II are true.
(d) Both statements I and II are false.
Answer: (b) Statement I is false and statement II is true.
Q10 Read the following statements: Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below:
Assertion (A) : Gifts received from abroad are not included in the estimation of domestic income but are included in the estimation of national income.
Reason (R) : National income includes only factor income.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Answer: (d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Q11 (a) All machines are not Capital goods. Describe.
(b) Sales of petrol and diesel cars are rising particularly in big cities. Analyze its impact on Gross domestic Product (GDP) and Welfare.
Answer. (a) The end-use of the machines determines whether it is a Capital good or not. Capital goods are those fixed assets of the producers which are used in the process of production for several years and which are of high value. Therefore only those machines which are used for further production are capital goods.
Answer (b) Impact on GDP: GDP = Sales, in case there is no change in stocks during the year. Increase in sales of cars during the year indicates increase in GDP. Impact on Welfare: Rise in sale of cars leads to increase in consumption of petrol and diesel. Both these fuels cause emission of harmful gasses & carbon dioxide. It increases environmental pollution which adversely affects the welfare of the people.
Q12 Net factor income from abroad can never be negative.” Defend or refute the given statement with valid argument.
Answer. The given statement is refuted. Net factor income from abroad is the difference between factor income earned from the rest of the world and factor income paid to the rest of the world. If the value of factor income paid to the rest of the world is greater than the factor income earned from the rest of the world, the resulting value (net factor income from abroad) can be negative.
Q13 (a) Discuss briefly how the money received from the sale of a second-hand car will be undertaken in estimation of National Income.
(b) Define the problem of double counting in the estimation of National Income.
Discuss two approaches to correct the problem of double counting.
Answer. (a) The money received from the sale of a second hand car will not be included in the national income of the country as it does not contribute to the current flow of goods in the economy. The value of that car has been counted in national income in the manufacturing year.
Answer (b) Problem of double counting in the estimation of National Income arises due to counting the value of commodities more than once. This leads to overestimation of the value of goods and services produced in the economy. Two approaches to correct the problem of double counting are-
(i) Final Output Method: According to this method, value of only the final goods and services should be added to determine the national income.
ii) Value Added Method: According to this method, sum total of the value added by each producing unit should only be taken in consideration. It means the value of intermediate consumption should not be considered.
Q14 During a given year the nominal national income increased by 14 percent while the real national income increased by only 6 percent. Population increased by 2 per cent. What has caused the difference between nominal income and real income? How much increase in real per capita income?
Answer. (i) Change in nominal income over a year is on account of
(a) change in quantity of goods and services and
(b) change in price level.
However, change in real income refers to change in quantity of goods and services only.
(ii) Therefore, a change of 14 percent in nominal income over the year is partly on
account of 6 percent change in quantity of goods and services and the remaining 8 per
cent must be on account of rise in general price level.
(iii) Real per capita income rise = Rise in real national income – Rise in population
= 6 – 2 = 4 percent.
Q15 ‘Circular flow of income in a two sector economy is based on the axiom that one’s expenditure is other’s income’. Do you agree with the given statement? Support your answer with valid reasons.
Answer. Yes, the given statement is correct. In a two sector economy, the firms produce goods and services and make factors payments to the households. The factor income earned by the households will be used to buy the goods and services which would be equal to the income of firms. The aggregate consumption expenditure by the households in the economy is equal to the aggregate expenditure on goods and services produced by the firms in the economy (Income of the producers).
Q16. “Management of a water polluting oil refinery says that it (oil refinery) ensures welfare through its contribution to Gross Domestic product.” Defend or refute the argument of management with respect to GDP as a welfare measure of the economy.
Answer. No, the given statement is not true. The value added by oil refinery to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) may also be polluting the nearby source of water. Such harmful effects that the refinery is causing to people and marine life is not penalized for the same. Thus, these negative externalities are not ensuring the welfare of the economy through Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
Q17 (a) Suppose a ban is imposed on consumption of tobacco. Examine its likely effects on gross domestic product and welfare.
(b) “Higher Gross Domestic Product (GDP) means greater per capita availability of goods in the economy.” Do you agree with the given statement? Give valid reasons in support of your answer.
Answer. (a) Ban on consumption of tobacco will bring down production of tobacco. Since it is counted in GDP, GDP will fall. The ban will improve health in general. It will thus increase welfare.
(b) “Higher Gross Domestic Product (GDP) means greater per capita availability of goods in the economy.” This statement is not always true.
(i) If the rate of population growth is more than the rate of growth of GDP, the per capita availability of goods and services will fall.
(ii) GDP doesn’t account for changes in inequalities in distribution of Income. If the rising GDP is concentrated in a few hands, per capita availability of goods in the economy might not increase.
Q18 (a) Define circular flow of income.Explain the phases of Circular flow of income.
(b) Write the difference between stock and flow. Give examples.
Answer. (a) Circular flow of income : Circular flow of income is how income is generated in the production process, then gets distributed among factors of production and ultimately gets disposed of in the form of consumption expenditure on goods and services by households. Phases of Circular flow of income
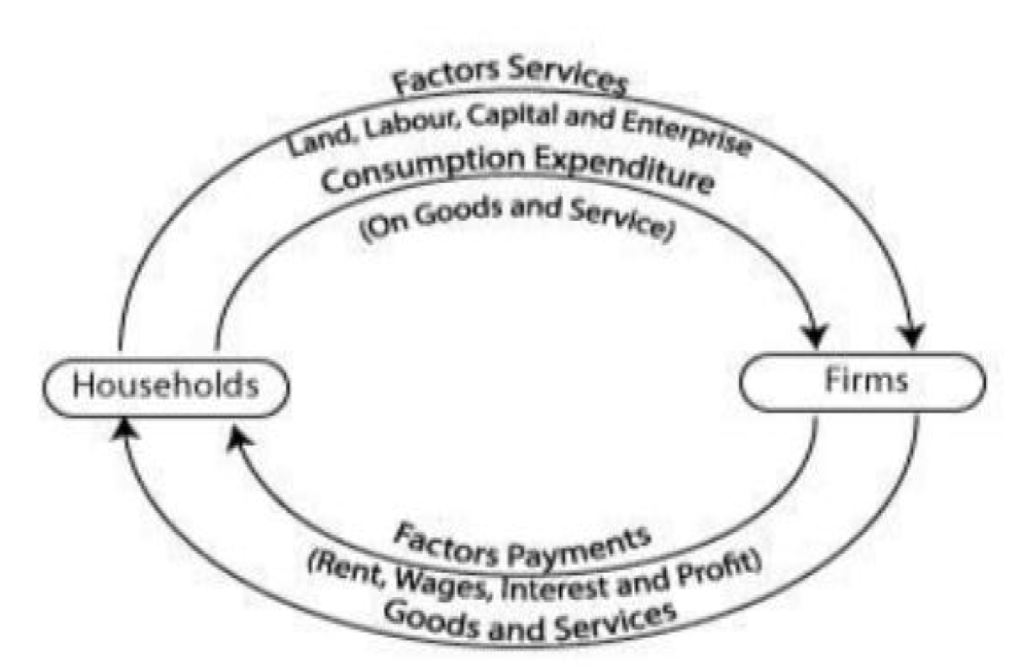
- Generation phase – income is generated in the production phase by firms.
- Distribution phase – income distributed among factors of production and flows from firms to households.
- Disposition phase – income is spent by households on goods and services and flows from households back to firms.
(b) Stock variable: stock variable is a variable whose magnitude is measured at a particular point of time. It is not time dimensional. Examples are capital, wealth, fixed assets, distance, population, money supply etc.
Flow variable: flow variable is a variable whose magnitude is measured during a given period of time. It is time dimensional. Examples are income,expenditure,export, import, GDP, production etc.
Q19 (a) Differentiate between final goods and intermediate goods with Example.
(b) Differentiate between Consumption/consumer goods and Capital goods with Example.
Answer. (a) Final goods – final goods are the goods which are purchased for consumption by consumers, households and for investment by firms. E.g. Milk purchased by consumers, machinery purchased by a firm etc. value of final goods is added to national income.
Intermediate goods – intermediate goods are the goods which are:
a. Purchased for resale purposes by a firm in the same year. Or
b. Completely used up in the production process.
Examples are milk purchased by a dairy, wheat purchased to make biscuits by a factory etc. Value of intermediate goods are not to be added to national income as these are included in the value of final goods. Adding value of intermediate goods in national income leads to the problem of double counting and overestimates the national income.
(b) Consumption/consumer goods – these are the final goods which satisfy the wants of consumers directly. For example wheat, clothes , washing machines purchased by consumers.
Capital goods- these are the final goods which help in the production of goods and services and have expected lifetime of more than one year. E.g tools and equipment , machinery purchased by firms etc.
Q 20 Define Consumption of fixed capital (depreciation), Gross Investment and Net Investment. Give the relationship among these.
Answer. Consumption of fixed capital (depreciation) : It is the fall in the value of fixed assets due to normal wear and tear and expected obsolescence. It can be calculated by dividing the value of fixed assets by its expected life in a number of years.
Gross Investment – it is the addition to the stock of capital of an economy during a given period of time.
Net Investment – it is the net addition to the stock of capital of an economy during a given period of time.
Net investment = gross investment – Consumption of fixed capital (depreciation).
Q 21 (a) What domestic territory includes? Who is normal resident of country?
(b) Give precautions while estimating national and domestic income.
Ans. (a)
1. Political frontiers including territorial water and airspace.
2. Ships and aircrafts operated by residents between two or more countries.
3. Fishing vessels, oil and natural gas rigs, floating platforms operated by residents in the international water.
4. Embassies, consulates and military establishments of the country located abroad.
Normal resident : normal resident refers to an individual or institution who ordinarily resides in a country and whose center of economic interest lies in that country.
*Citizens of other countries who reside in India for more than one year become normal
residents of India.
(b) Items not to be included in national income and domestic income. (PRECAUTIONS)
S – Second hand goods ‘sale and purchase (already counted in the NY of the year they were produced.)
W- Windfall gains like winning from lottery, horse race etc.(no contribution to flow of goods & services)
I – Intermediate goods value.( already included in the value of final goods.)
F – financial transactions like sales & purchase of shares, debentures(no contribution to flow of goods & services).
T – Transfer income and payments (no contribution to flow of goods & services)
Besides production of services for self consumption is not included (difficult to measure
market value) But, production of goods for self consumption is included (as it contribute
to current production)
Q 22 (a) Differentiate between Factor income and Transfer income with Example.
(b) Define National income(NNPfc) and Domestic income(NDPfc).
Answer. (a) Factor income– income which is received by factors of production for rendering their services in the production process. Factor income is included in national income. Examples are rent, wages, interest and profit.
Transfer income – income which is received without rendering productive services in return. It is not included in national income. Examples are old age pensions, scholarships etc.
Answer (b) National income(NNPfc):- it is the sum total of factor incomes generated by the normal residents of a country within the domestic territory of that country and in the rest of world during an accounting year. It includes NFIA.
Domestic income(NDPfc):- it is the sum total of factor incomes generated within the domestic territory of a country by residents and non residents during an accounting year. It does not include NFIA.
Q 23 Which of the following will be included in national income (give reasons)
- Commission and brokerage -( yes, these are productive services)
- Construction of flyovers, hospitals ,school, building – ( yes, these are part of
capital formation) - Free meals, clothes , bonus , rent free house, medical facilities, retirement
pension, salaries and wages in cash, to employees – ( yes , as these are part of
compensation of employees) - Dividend / undistributed profit – (yes ,as these are part of operating surplus).
- Interest paid by the firm to the bank -( yes, the interest has been paid on loan
taken for productive purposes. - Interest paid by the individual to the bank -(no ,the interest has been paid on loan
taken for consumption purpose. - Dividend received by Ram from a foreign company-( yes ,as it is a part of FIFA)
- Expenditure on advertisement/scientific research/entertainment allowance – (no
,as these are intermediate expenditures.) - Salaries paid to Indian working in US embassy in India– (Yes ,it is a part of FIFA)
- Dividend received by a foreigner from investment in Indian company -( No, as
it is FITA) - Old age pension/scholarships/remittances/GST – ( no, as these are transfer
income/payments) - Expenditure by government on street light , free medicines & education – (yes,
as these are part of government final consumption expenditure) - Purchase of trucks to transport goods by a company – (Yes, it is a part of the
gross domestic capital formation.) - Payment of fees to a lawyer engaged by a firm – (No, this is an intermediate
cost.)
Q 24 Which of the following will be included in domestic income (give reasons)
- Dividend received by Ram from a foreign company – ( no, as it is not generated in
the domestic territory of India) - Salaries paid to Indian working in USA embassy in India – (no, as it is not
generated in the domestic territory of India) - Dividend received by a foreigner from investment in Indian company – ( Yes, as
it is generated in the domestic territory of India) - Salaries paid to Japanese working in Indian embassy in Japan – (Yes ,as it is
generated in the domestic territory of India) - Domestic/household services performed by a woman – No, production of
services for self consumption is not included as it is difficult to measure market value. - Compensation to the victims of a cyclone – No, as it is transfer income.
Q 25 Differentiate between REAL GDP(GDP AT CONSTANT PRICE) and NOMINAL GDP(GDP AT CURRENT PRICE)
Answer:
| REAL GDP(GDP AT CONSTANT PRICE) or REAL NATIONAL INCOME | NOMINAL GDP(GDP AT CURRENT PRICE) or NOMINAL NATIONAL INCOME |
| GDP Measured at base year prices. | GDP Measured at current year prices. |
| Affected by change in quantity of physical output. | Affected by both change in price and quantity of physical output. |
| Measures the true performance of growth of the Economy | Not necessarily measures true performance of growth of the Economy. |
Real GDP = (Nominal GDP X 100 / GDP Deflator)
Real National income = (Nominal National income X 100 / price index)
Q 26 GDP as a true indicator of welfare but has some limitations. Explain
Answer. GDP as a true indicator of welfare has following limitations:
1. Affected by changes in price : Without any increase in real output GDP can increase due to increase in price.
2. Distribution of GDP : GDP does not ensure that goods and services are evenly distributed in an economy or not. If there are large numbers of poor people in country with high GDP, how can it be said to be a true indicator of the welfare of people?
3. Composition of GDP : if any increase in GDP is due to increase in the production of war ammunition , liquor etc. then welfare of people may not increase.
4. Externalities : there are two types of externalities.
(a) Positive externalities – Positive externalities refer to benefits caused by one entity to another, without being paid for it. Like parks for which people don’t pay but it increases their welfare.
(b) Negative externalities – negative externalities refer to the harms caused by one entity to another, without being penalized for it. Like Pollution produced by a factory. GDP doesn’t take into account positive and negative externalities but the welfare of people is affected.
5. Non monetary transactions : non monetary transactions like services of housewife, kitchen gardening are not included in the estimation of GDP , because their market value is difficult to estimate. But these transactions increase the welfare of people.
